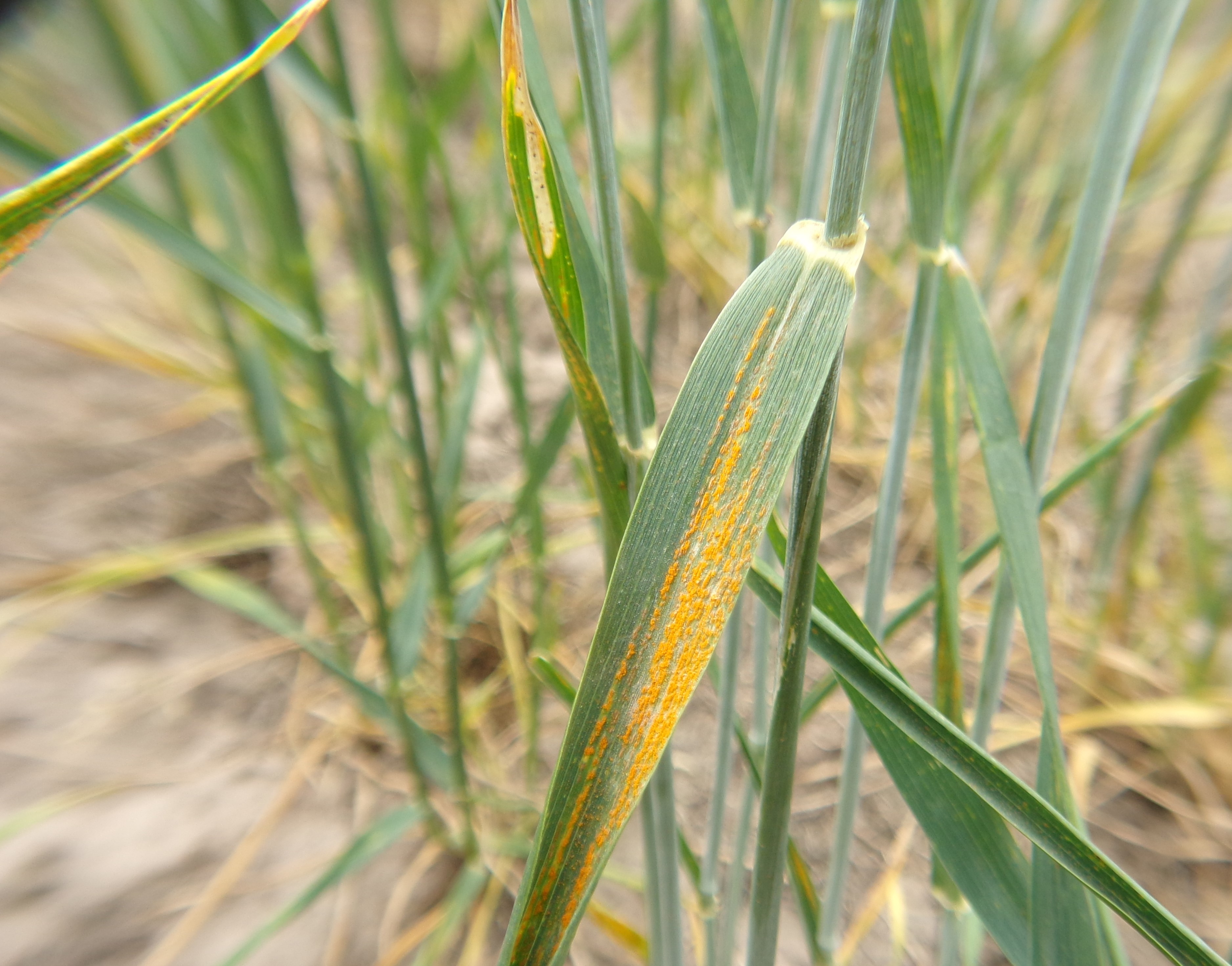
Effect on wheat (Triticum aestivum) yield of the yellow rust caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici and its effect on yield
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15517/am.v33i1.46141Keywords:
foliage disease, wheat cultivars, foliar fungicidesAbstract
Introduction. In recent years, yellow rust caused by Puccinia striiformis was the most prevalent disease in wheat (Triticum aestivum), in the north of the province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. Objective. To evaluate the progress of yellow rust in wheat cultivars, with and without foliar fungicide application and its effect on yield and its components. Materials and methods. This study was carried out during two consecutive years (2017 and 2018) in the town of Junín, Buenos Aires, Argentina, on nineteen wheat cultivars, with and without foliar fungicide application. The damages of yellow rust on yield and industrial quality were quantified. Likewise, the evolution of the disease was evaluated using the area under the disease intensity progress curve (ABCPIE). The ABCPIE was associated with the yield, its components, and hectoliter weight. Results. Of all the variables analyzed, the ABCPIE had a significant interaction (p<0.05) between the foliar fungicide application and the cultivar used. The cultivars Lapacho, Minerva, MS 415, and SY 211 were resistant to yellow rust. The cultivar most susceptible to the disease was Algarrobo. The application of foliar fungicide, with low levels of the disease, significantly reduced its evolution, as reflected from the area under the disease intensity progress curve. Conclusion. The evolution over time of the yellow rust caused by P. striiformis depended on the genetic behavior of the cultivar and the application of foliar fungicide. The cultivars that had the highest yields, lowest ABCPIE, and highest hectoliter weight were: Lapacho, SY 11, BIO 1006, and Minerva.
Downloads
References
Agrios, G. N. (2005). Plant pathology (5th Ed.). Academic Press.
Barrio, M., Lavilla, M. A., Beltrán, G., Ivancovich, A., & Pepper, A. (2020). Evaluación del momento óptimo de aplicación de fungicida foliar para el control de roya amarilla. Revista Técnica Cultivos de Invierno, 2020, 107-111.
Bolsa de cereales. (2021, 18 de febrero). Estimaciones agrícolas. https://www.bolsadecereales.com/estimaciones-informes
Campos, P. E. (2017). Identificación de razas exóticas de roya amarilla en región triguera Argentina. Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Agropecuaria.
Di-Rienzo, J. A., Casanoves, F., Balzarini, M. G., González, L., Tablada, M., & Robledo, C. W. (2011). InfoStat. Grupo InfoStat. http://www.infostat.com.ar
Cordo, C. A. (2014). Enfermedades del trigo. Avances científicos en la Argentina. Editorial de la Universidad de La Plata.
Hovmøller, M. S., Justesen, A. F., & Brown, J. K. M. (2002). Clonality and long-distance migration of Puccinia striiformis f.sp. tritici in north-west Europe. Plant Pathology, 51(1), 24-32. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3059.2002.00652.x
Julca-Otiniano, A., Borjas Ventura, R., Alvarado Huamán, L., Julca Vera, N., Castro Cepero, V., & Bello Ames, S. (2019). Relación entre la incidencia y la severidad de la roya del café (Hemileia vastatrix) en San Ramón, Chanchamayo, Perú. Journal of Science and Research, 4(4), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3477556
O’Brien, L., Brown, J. S., Panozzo, J. F., & Archer, M. J. (1990). The effect of stripe rust on the quality of Australian wheat varieties. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 41(5), 827-833. https://doi.org/10.1071/ar9900827
Rice, J. A. (1995). Mathematical statistics and data analysis. (2nd Ed.). Duxbury Press.
Shahin, A., Ashmawy, M., El-Orabey, W., & Esmail, S. (2020). Yield losses in wheat caused by stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis) in Egypt. American Journal of Life Sciences, 8(5), 127-134. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajls.20200805.17
Vergara-Diaz, O., Kefauver, S. C., Elazab, A., Nieto-Taladriz, M. T., & Araus, J. L. (2015). Grain yield losses in yellow-rusted durum wheat estimated using digital and conventional parameters under field conditions. The Crop Journal, 3(3), 200-210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2015.03.003
Wiese, M. V. (2000). Compendio de enfermedades del trigo. Hemisferio Sur Editorial.
Zadoks, J. C., Chang, T. T., & Konzak, C. F. (1974). A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Research, 14(6), 415-421. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3180.1974.tb01084.x

Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
1. Proposed policy for open access journals
Authors who publish in this journal accept the following conditions:
a. Authors retain the copyright and assign to the journal the right to the first publication, with the work registered under the attribution, non-commercial and no-derivative license from Creative Commons, which allows third parties to use what has been published as long as they mention the authorship of the work and upon first publication in this journal, the work may not be used for commercial purposes and the publications may not be used to remix, transform or create another work.
b. Authors may enter into additional independent contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the article published in this journal (e.g., including it in an institutional repository or publishing it in a book) provided that they clearly indicate that the work was first published in this journal.
c. Authors are permitted and encouraged to publish their work on the Internet (e.g. on institutional or personal pages) before and during the review and publication process, as it may lead to productive exchanges and faster and wider dissemination of published work (see The Effect of Open Access).