The effect of processing and storage on Klanceng honey (Tetragonula laeviceps)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15517/am.v34i2.52131Keywords:
heating, invertase, diastase, honey qualityAbstract
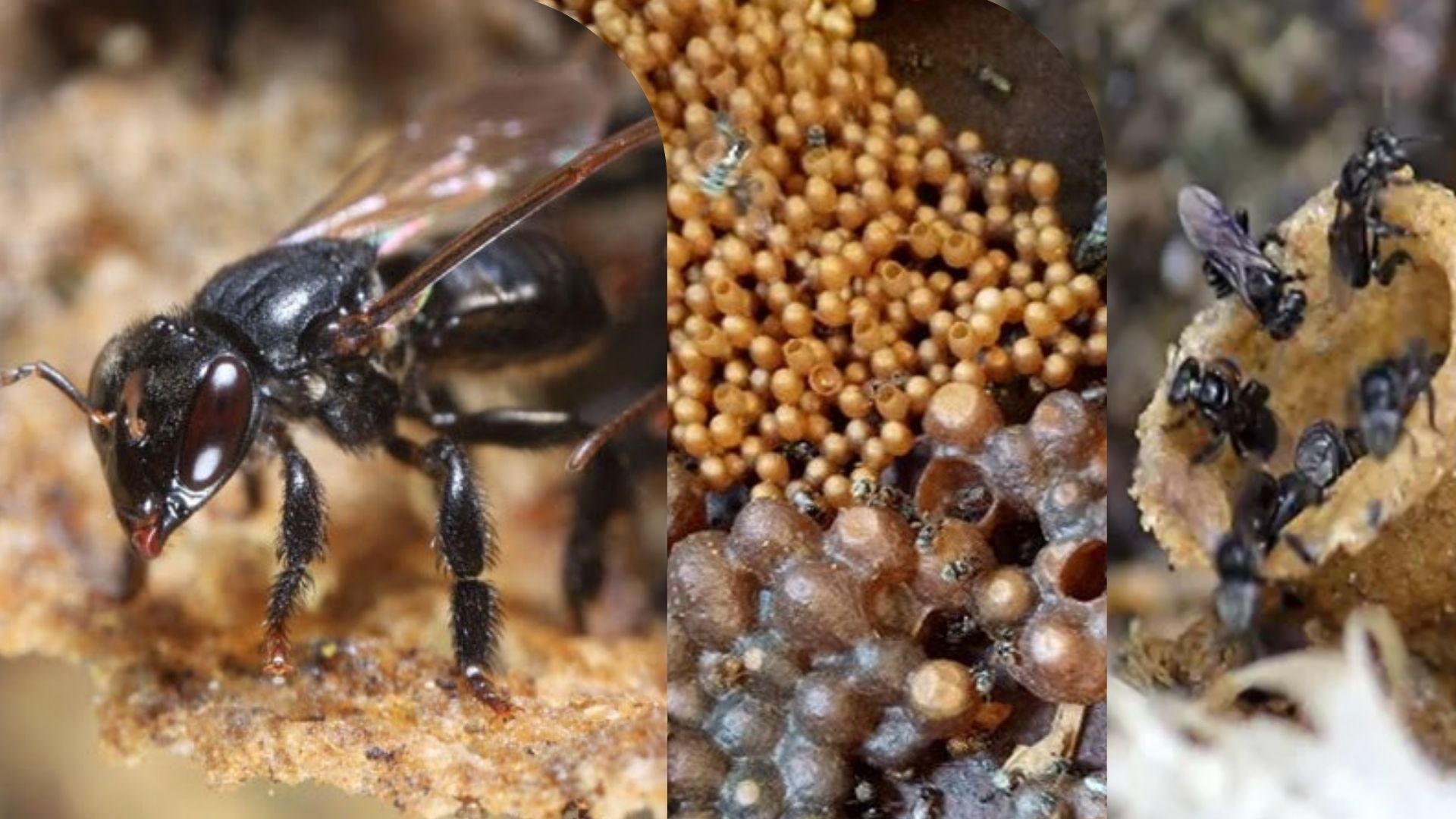
Introduction. Klanceng honey (Tetragonula laeviceps) is in great demand because of its benefits. There is no information on the expiration date of the Klanceng honey. Objective. To predict the shelf life of Klanceng honey by evaluating the effect of heating (40 ºC / 48 h and 70 ºC / 7 h) and storage for two years. Materials and methods. The analysis was carried out three times (2020, 2021, and 2022) at the National Innovation Research Agency Laboratory, Jakarta, Indonesia. Samples of Klanceng honey (Tetragonula laeviceps) were taken from a bee farm in Magetan, East Java, Indonesia. The sample (5 kg) was divided into 3: without heating process (UT), heating at 40 ºC / 48 h (T1), and heating at 70 ºC / 7 h (T2). Then analyzed the activity of HMF, diastase, invertase, acid phosphatase (AP), glucose oxidase (GO), DPPH, honey color, and phenolic at 0, 12 and 24-months. Results. The results showed that short heating at high temperature (70 ºC / 7 h) had a greater impact on decreasing enzyme activity compared to prolonged heating at low temperature (40 ºC / 48 h). Storage had a major impact on the increase of 5-hydroxymethyl (furan)-2-carbaldehyde (HMF) compared to the heating process. During storage (24-months) the HMF value exceeded the maximum limit. Conclusions. The HMF value (55.33 ± 0.57 mg/kg) exceeded the maximum allowable limit (max 40 ppm), this was due to the significant effect of heating on T2 and the storage process. The shelf life of Klanceng honey was two years, as long as it was not heated to high temperatures (70 ºC).
Downloads
References
Abou-Shaara, H. F., Owayss, A. A., Ibrahim, Y. Y., & Basuny, N. K. (2017). A review of impacts of temperature and relative humidity on various activities of honey bees. Insectes Sociaux, 64(4), 455–463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-017-0573-8
Agus, A., Agussalim, N., Umami, N., & Budisatria, I. G. S. (2019). Evaluation of antioxidant activity, phenolic, flavonoid and vitamin C content of several honeys produced by the Indonesian stingless bee: Tetragonula laeviceps. Livestock Research for Rural Development, 31(10), Article 152. http://www.lrrd.org/lrrd31/10/aguss31152.html
Agus, A., Agussalim, Sahlan, M., & Sabir, A. (2021). Honey sugars profile of stingless bee Tetragonula laeviceps (Hymenoptera: Meliponinae). Biodiversitas, 22(11), 5205–5210. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d221159
Agussalim, Agus, A., Umami, N., & Suparta Budisatria, I. G. (2017, September 12-14). The effect of daily activities stingless bees of Trigona sp. on honey production. In Universitas Gadjah Mada Yogyakarta (Ed.), Proceedings of the 7th International Seminar on Tropical Animal Production (pp. 223–227). Indonesian Society for Sustainable Tropical Animal Production. https://journal.ugm.ac.id/istapproceeding/article/viewFile/29838/17967
Akalın, H., Bayram, M., & Ertan Anlı, R. (2017). Determination of some individual phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of mead produced from different types of honey. Journal of The Institute of Brewing, 123(1), 167–174. https://doi.org/10.1002/jib.396
Akhmazillah Fauzi, N., & Mehdi Farid, M. (2017). High pressure processed Manuka honey: Change in nutritional and rheological properties over 1-year storage. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 41(4), Article e13085. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.13085
Akhmazillah, M. F. N., Farid, M. M., & Silva, F. V. M. (2013). High pressure processing (HPP) of honey for the improvement of nutritional value. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 20, 59–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2013.06.012
Al Kafaween, M. A., Hilmi, A. B. M., Khan, R. S., Bouacha, M., & Amonov, M. (2019). Effect of Trigona honey on Escherichia coli cell culture growth: In vitro study. Journal of Apitherapy, 5(2), 10–17. https://www.japitherapy.com/abstract/effect-of-trigona-honey-on-escherichia-coli-cell-culture-growth-in-vitro-study-47330.html
Al-kafaween, M. A., Hilmi, A. B. M., Jaffar, N., Al-Jamal, H. A. N., Zahri, M. K., & Jibril, F. I. (2020). Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of Malaysian Trigona honey against Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 10145 and Streptococcus pyogenes ATCC 19615. Jordan Journal of Biological Science, 13(1), 69–76. https://jjbs.hu.edu.jo/files/vol13/n1/Paper%20Number%2011.pdf
Al-Rubaie, W. K., & Al-Fekaiki, D. F. (2022). Enzymes activity study of multiple types of Iraqi honey. Journal of Pharmaceutical Negative Results, 13(Special 2), 255–260. https://doi.org/10.47750/pnr.2022.13.S02.36
Amariei, S., Norocel, L., & Scripcă, L. A. (2020). An innovative method for preventing honey crystallization. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 66, Article 102481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2020.102481
Association of Official Analytical Chemists. (2016). Official methods of analysis of AOAC International (20th ed.). AOAC International.
Beretta, G., Granata, P., Ferrero, M., Orioli, M., & Facino, R. M. (2005). Standardization of antioxidant properties of honey by a combination of spectrophotometric/fluorimetric assays and chemometrics. Analytica Chimica Acta, 533(2), 185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2004.11.010
Cao, W., Zhang, J. J., Liu, C. Y., Bai, W. S., & Cheng, N. (2020). A modified Folin-Ciocalteu method for the microdetermination of total phenolic content in honey. International Food Research Journal, 27(3), 576–584. https://bit.ly/3OqxKoc
Castro-Vázquez, L., Alañon, M. E., Gonzalez-Viñas, M. A., & Pérez-Coello, M. S. (2012). Changes in the volatile fractions and sensory properties of heather honey during storage under different temperatures. European Food Research and Technology, 235(2), 185–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-012-1756-1
Cozmuta, A. M., Cozmuta, L. M., Varga, C., Marian, M., & Peter, A. (2011). Effect of thermal processing on quality of polyfloral honey. Romanian Journal of Food Science, 1(1), 45–52.
Erdtman, G. (1954). An introduction to pollen analysis, Waltham, Mass. Chronica Botanica Company.
Fatima, I. J., Mohd Hilm, A. B., Salwani, I., & Lavaniya, M. (2018). Physicochemical characteristics of malaysian stingless bee honey from trigona species. IIUM Medical Journal Malaysia, 17(1), Article 1030. https://doi.org/10.31436/imjm.v17i1.1030
Haouam, L., Dailly, H., Bruneau, E., & Tahar, A. (2019). The quality of honeys influenced by the traditional heating method. Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Food Sciences, 8(6), 1276–1280. https://doi.org/10.15414/jmbfs.2019.8.6.1276-1280
Indonesian National Standard. (2021). SNI-3545-2013. SNI untuk Jamin Kualitas Mutu Maadu. https://bit.ly/3UNQdgx
International Honey Commission (Ed.). (2009). Harmonised methods of the International Honey Commision. http://www.ihc-platform.net/ihcmethods2009.pdf
Karabournioti, S., & Zervalaki, P. (2001). The effect of heating on honey HMF and invertase. Apiacta, 36(4), 177–181.
Kekeçoğlu, M., Çaprazlı, T., Çalışkan, E., & Uğraş, S. (2022). Determination of therapeutic values of Düzce / Yığılca honeys by underlining overlooked parameters. Turkish Journal of Agriculture - Food Science and Technology, 10(2), 299–308. https://doi.org/10.24925/turjaf.v10i2.299-308.4823
Machado De-Melo, A. A., de Almeida-Muradian, L. B., Sancho, M. T., & Pascual-Maté, A. (2018). Composición y propiedades de la miel de Apis mellifera: una revisión. Journal of Apicultural Research, 57(1), 5–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/00218839.2017.1338444
Makhloufi, C., Taïbi, K., & Ait Abderrahim, L. (2020). Characterization of invertase and diastase activities, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural content and hydrogen peroxide production of some Algerian honeys. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions A: Science, 44(5), 1295–1302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-020-00936-x
Maurizio, A. (1975). In honey: A comprehensive survey. Heinemann, London.
Missio da Silva, P., Valdemiro Gonzaga, L., Stremel de Azevedo, M., Biluca, F. C., Schulz, M., Oliveira Costa, A. C., & Fett, R. (2020). Stability of volatile compounds of honey during prolonged storage. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 57, 1167–1182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04163-0
Molyneux, P. (2004). The use of the stable free radical diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (DPPH) for estimating antioxidant activity. Songklanakarin Journal of Science and Technology, 26(2), 211–219. https://sjst.psu.ac.th/article.php?art=214
Nagai, T., Kai, N., Tanoue, Y., & Suzuki, N. (2018). Chemical properties of commercially available honey species and the functional properties of caramelization and Maillard reaction products derived from these honey species. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 55(2), 586–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2968-y
Ng, W. J., Chan, Y. J., Lau, Z. K., Lye, P. Y., & Ee, K. Y. (2017). Antioxidant properties and inhibitory effects of trigona honey against staphylococcus aureus planktonic and biofilm cultures. International Journal of GEOMATE, 13(37), 28–33. http://doi.org/10.21660/2017.37.2703
Nguyen, L. T., Balasubramaniam, V. M., & Sastry, S. K. (2012). Determination of in-situ thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, volumetric specific heat and isobaric specific heat of selected foods under pressure. International Journal of Food Properties, 15(1), 169–187. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942911003754726
Nugroho, R. B., & Soesilohadi, H. (2014). Identifikasi Macam Sumber Pakan Lebah Trigona sp (Hymenoptera: Apidae) di Kabupaten Gunungkidu. BioMedika, 7(2), 42–45. http://ejurnal.setiabudi.ac.id/ojs/index.php/biomedika/article/view/184
Oddo, L. P., Heard, T. A., Rodríguez-Malaver, A., Pérez, R. A., Fernández-Muiño, M., Sancho, M. T., Sesta, G., Lusco, L., & Vit, P. (2008). Composition and antioxidant activity of Trigona carbonaria honey from Australia. Journal of Medicinal Food, 11(4), 789–794. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2007.0724
Önür, İ., Misra, N. N., Barba, F. J., Putnik, P., Lorenzo, J. M., Gökmen, V., & Alpas, H. (2018). Effects of ultrasound and high pressure on physicochemical properties and HMF formation in Turkish honey types. Journal of Food Engineering, 219, 129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.09.019
Pasias, I. N., Kiriakou, I. K., Kaitatzis, A., Koutelidakis, A. E., & Proestos, C. (2018). Effect of late harvest and floral origin on honey antibacterial properties and quality parameters. Food Chemistry, 242, 513–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.083
Pohl, P., Sergiel, I., & Stecka, H. (2009). Determination and fractionation of metals in honey. Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry, 39(4), 276–288. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408340903001250
Sabir, A., Agus, A., & Sahlan, M. (2021). The minerals content of honey from stingless bee Tetragonula laeviceps from different regions in Indonesia. Livestock Research for Rural Development, 33(2), Article 22. http://www.lrrd.org/lrrd33/2/aguss3322.html
Samborska, K., Langa, E., & Bakier, S. (2015). Changes in the physical properties of honey powder during storage. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 50(6), 1359–1365. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.12797
Singh, I., & Singh, S. (2018). Honey moisture reduction and its quality. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 55(10), 3861–3871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3341-5
Syam, Y., Usman, A. N., Natzir, R., Rahardjo, S. P., Hatta, M., Sjattar, E. L., Saleh, A., & Sa, M. (2016). Nutrition and pH of Trigona honey from Masamba, South Sulawesi, Indonesia. International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research, 27(1), 32–36. https://gssrr.org/index.php/JournalOfBasicAndApplied/article/view/5697
Tomazic, B. B. (2001). Physicochemical principles of cardiovascular calcification. Zeitschrift Für Kardiologie, 90(3), 68–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003920170046
Tosi, E. A., Ré, E., Lucero, H., & Bulacio, L. (2004). Effect of honey high-temperature short-time heating on parameters related to quality, crystallisation phenomena and fungal inhibition. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 37(6), 669–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2004.02.005
Trinder, P. (1969). Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with an alternative oxygen acceptor. Annals of Clinical Biochemistry, 6(1), 24–27. https://doi.org/10.1177/000456326900600108
Von Der Ohe, W., Oddo, L. P., Piana, M. L., Morlot, M., & Martin, P. (2004). Harmonized methods of melissopalynology. Apidologie, 35(Suppl. 1), S18–S25. https://doi.org/10.1051/apido:2004050
Vorlova, L., & Pridal, A. (2002). Invertase and diastase activity in honeys of Czech provenience. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Sbornik Mendelovy Zemedelske a Lesnicke Mendelianae Brunensis, 5(8), 57–66.
Wingenroth, M. C. (2001 October 28 - November 1). Honey types and pollen grains of Asuncion Lavalle, Mendoza, Argentina, vegetal origin and possible management of the beehive production. 37th International Apicultural Congress, Durban, South Africa.
Zulkan Jayadi, L., & Susandarini, R. (2020). Melissopalynological analysis of honey produced by two species of stingless bees in Lombok Island, Indonesia. Nusantara Bioscience, 12(2), 97–108. https://doi.org/10.13057/nusbiosci/n120203

Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Bundianto, Diah Kusmardini, Zefki Okta Feri, Muh Jaenal Arifin, Anik Suparmi, Kiki Kristiani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. Proposed policy for open access journals
Authors who publish in this journal accept the following conditions:
a. Authors retain the copyright and assign to the journal the right to the first publication, with the work registered under the attribution, non-commercial and no-derivative license from Creative Commons, which allows third parties to use what has been published as long as they mention the authorship of the work and upon first publication in this journal, the work may not be used for commercial purposes and the publications may not be used to remix, transform or create another work.
b. Authors may enter into additional independent contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the article published in this journal (e.g., including it in an institutional repository or publishing it in a book) provided that they clearly indicate that the work was first published in this journal.
c. Authors are permitted and encouraged to publish their work on the Internet (e.g. on institutional or personal pages) before and during the review and publication process, as it may lead to productive exchanges and faster and wider dissemination of published work (see The Effect of Open Access).