Isolated yeasts from bioferments of mountain microorganisms, an option for plant nutrition
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15517/am.2023.52527Keywords:
biofertilizer, auxins, phosphorus, potassium, solubilizationAbstract
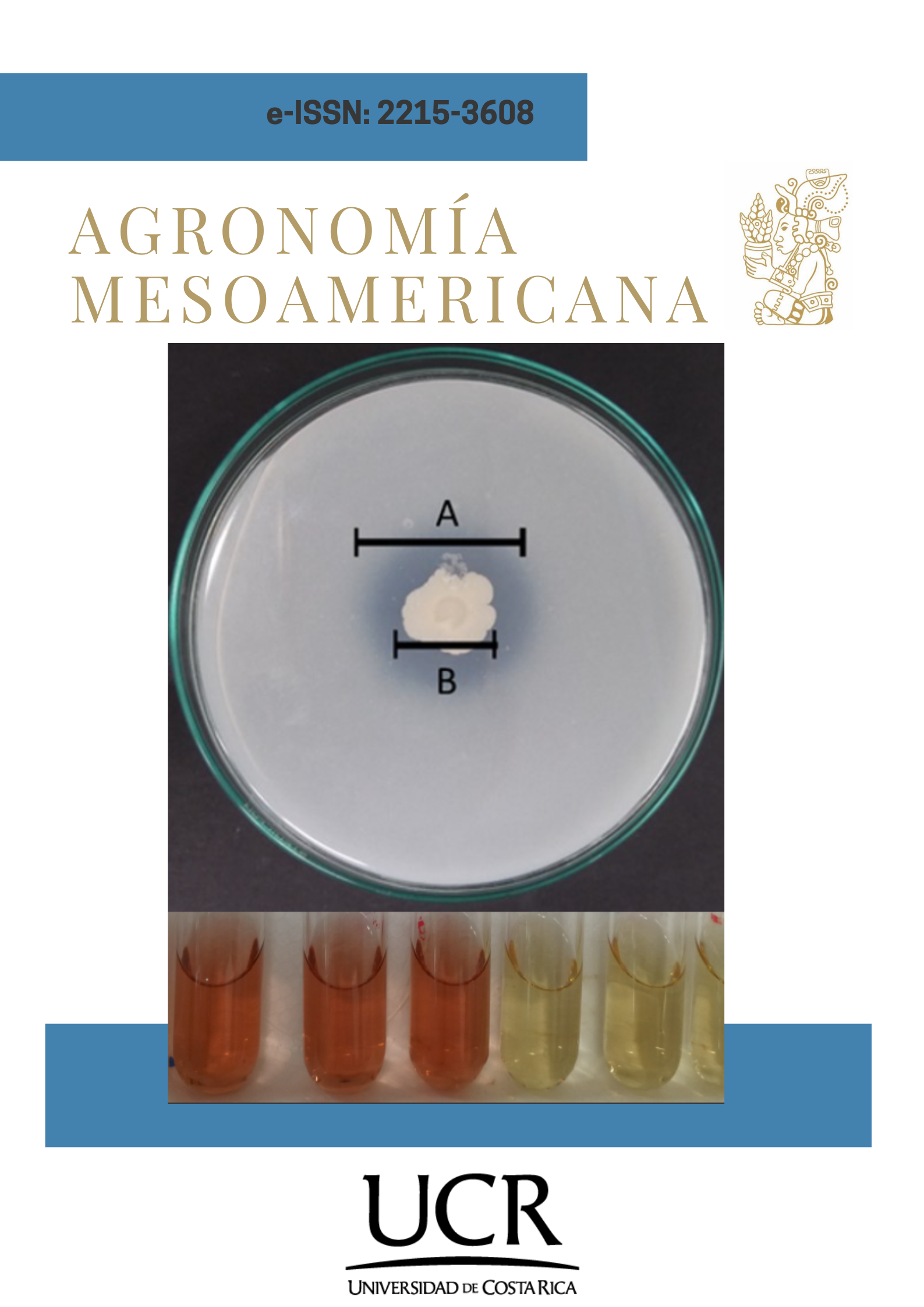
Introduction. Phosphorus and potassium are essential nutrients for plant development; however, they are scarcely available in soil, making chemical or mineral fertilization necessary, an inefficient practice due to the absence of solubilizing microorganisms. The application of Mountain Microorganisms (MM) bioferments is an alternative, however, few studies show the agronomic potential of the yeasts present in this type of bioferments. Objective. To evaluate, at in vitro level, the biofertilizing and growth-promoting capacity of antagonist yeasts isolated from MM bioferments. Materials and methods. This research was carried out in 2019 at the University of Medellín, Colombia. The biofertilizing capacity was determined by measuring the solubilization of phosphorus and potassium in solid media by measuring the solubilization halos and in a liquid medium by quantifying phosphorus (PS) and soluble potassium (KS) in mg per liter of soluble mineral. The growth-promoting activity was determined by quantifying the production of acetic indole (AIA) of yeasts isolated from MM. As an additional test, the production capacity of cellulases was evaluated in a carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) media. Results. On day six, the highest concentrations of PS and KS in liquid medium were evidenced. Both in NBRIP agar and broth with P rock, the isolate GRB-LB05 showed a PS of 3.57 mg L-1 different from the control. In modified NBRIP agar and feldspar broth, GRB-LB01 had the lowest pH and a low KS concentration, while GRB-LB12 (1.32 mg L-1) and GRB-LB02 (1.12 mg L-1) registered the highest concentrations of KS. GRB-LB06 yeast was the most promising IAA-producing isolate (12 mg L-1), followed by GRB-LB13. Conclusions. The antagonistic yeasts isolated from liquid MM bioferments showed biofertilizing and growth-promoting capacity, with GRB-LB12 (Suhomyces xylopsoci) being the one that stands out in the solubilization of P, K, IAA production and cellulolytic capacity.
Downloads
References
A’Bear, A. D., Jones, T. H., & Boddy, L. (2014). Size matters: What have we learnt from microcosm studies of decomposer fungus–invertebrate interactions? Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 78, 274–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.08.009
Alavaisha, E., Manzoni, S., & Lindborg, R. (2019). Different agricultural practices affect soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorous in Kilombero -Tanzania. Journal of Environmental Management, 234, 159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.12.039
Altınbay Izgu, D., Aysun Kepekci, R., & Izgu, F. (2011). Inhibition of Penicillium digitatum and Penicillium italicum in vitro and in planta with Panomycocin, a novel exo-β-1,3-glucanase isolated from Pichia anomala NCYC 434. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 99(1), 85–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9527-0
Asoegwu, C. R., Awuchi, C. G., Nelson, K. C. T., Orji, C. G., Nwosu, U. O., Egbufor, U. C., & Awuchi, C. G. (2020). A Review on the role of biofertilizers in reducing soil pollution and increasing soil nutrients. Himalayan Journal of Agriculture, 1(1), 34–38. https://himjournals.com/article/articleID=50
Bagyalakshmi, B., Ponmurugan, P., & Balamurugan, A. (2017). Potassium solubilization, plant growth promoting substances by potassium solubilizing bacteria (KSB) from southern Indian Tea plantation soil. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 12, 116–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2017.09.011
Bashan, Y., Kamnev, A. A., & de-Bashan, L. E. (2013). Tricalcium phosphate is inappropriate as a universal selection factor for isolating and testing phosphate-solubilizing bacteria that enhance plant growth: a proposal for an alternative procedure. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 49, 465–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-012-0737-7
Boontham, W., Srivanichpoom, N., Nutaratat, P., Limtong, S., & Srisuk, N. (2019). Enhanced production of phytase, a feed enzyme, from Pichia kudriavzevii using mutagenesis and improved culture conditions. Chiang Mai Journal of Science, 46(3), 431–443. https://epg.science.cmu.ac.th/ejournal/dl.php?journal_id=10134
Boubekri, K., Soumare, A., Mardad, I., Lyamlouli, K., Hafidi, M., Ouhdouch, Y., & Kouisni, L. (2021). The screening of potassium-and phosphate-solubilizing actinobacteria and the assessment of their ability to promote wheat growth parameters. Microorganisms, 9(3), Article 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030470
Borges de Oliveira, T., Bizarria Junior, R., Godoi Silva, L., & Rosa-Magri, M. M. (2019). Rhizosphere yeast Torulaspora globosa with plant growth promotion traits and improvement of the development of tomato seedlings under greenhouse conditions. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 14(22), 935–942. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR2019.13950
Buzdar, M. A., Chi, Z., Wang, Q., Hua, M. -X., & Chi, Z. -M. (2011). Production, purification, and characterization of a novel killer toxin from Kluyveromyces siamensis against a pathogenic yeast in crab. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 91, 1571–1579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3220-8
Campo-Martínez, A. del P., Acosta-Sanchez, R. L., Morales-Velasco, S., & Prado, F. A. (2014). Evaluación de microrganismos de montaña (MM) en la producción de acelga en la meseta de Popayán. Biotecnología en el Sector Agropecuario y Agroindustrial, 12(1), 79-87. https://revistas.unicauca.edu.co/index.php/biotecnologia/article/view/322
Celis Bautista, L. X., & Gallardo, I. R. (2008). Estandarización de métodos de detección para promotores de crecimiento vegetal (ácido indol acético y giberelinas) en cultivos microbianos [Tesis de Grado, Pontificia Universidad Javeriana]. Repositorio de la Pontificia Universidad Javeriana. https://repository.javeriana.edu.co/handle/10554/8948
Din, M., Nelofer, R., Salman, M., Abdullah, Hayat Khan, F., Khan, A., Ahmad, M., Jalil, F., Ud Din, J., & Khan, M. (2019). Production of nitrogen fixing Azotobacter (SR-4) and phosphorus solubilizing Aspergillus niger and their evaluation on Lagenaria siceraria and Abelmoschus esculentus. Biotechnology Reports, 22, Article e00323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00323
Fikrinda, F., Susanna, S., Khalil, M., Sriwati, R., Syafruddin, S., & Sufardi, S. (2020). Characterization and pathogenicity test of indigenous cellulolytic fungi as biofertilizer candidate. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 486, Article 012126. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/486/1/012126
Flatian, A. N., Anas, I., Sutandi, A., & Ishak. (2021). The ability of some microbes to solubilize the hardly soluble phosphorous and potassium from various sources in vitro. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 648, Article 012143. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/648/1/012143
Hernández-Hernández, E. J., Hernández-Ríos, I., Almaraz-Suarez, J. J., López-López, A., Torres-Aquino, M., & Morales-Flores, F. J. (2018). Caracterización in vitro de rizobacterias y su antagonismo con hongos causantes del damping off en chile. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Agrícolas, 9(3), 525–537. https://doi.org/10.29312/remexca.v9i3.335
Hernández-Fernández, M., Cordero-Bueso, G., Ruiz-Muñoz, M., & Cantoral, J. M. (2021). Culturable yeasts as biofertilizers and biopesticides for a sustainable agriculture: A comprehensive review. Plants, 10(5), Article 822. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050822
Hernández-Leal, T. I., Carrión, G., & Heredia, G. (2011). Solubilización in vitro de fosfatos por una cepa de Paecilomyces lilacinus (Thom) Samson. Agrociencia, 45(8), 881–892. https://www.agrociencia-colpos.org/index.php/agrociencia/article/view/925
IBM Corporation. (2017). IBM SPSS Statistics para Windows (version 25.0). IBM Corp.
Jacques, N., & Casaregola, S. (2019). Large biodiversity of yeasts in French Guiana and the description of Suhomyces coccinellae f.a. sp. nov. and Suhomyces faveliae f.a. sp. nov. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 69(6), 1634–1649. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003369
Jeberlin Prabina, B., Kumutha, K., Anandham, R., & Durga, P. (2019). Isolation and characterization of multifunctional yeast as plant probiotics for better crop nutrition in pulses. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 8(1), 2711–2718. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2019.801.286
Karmakar, P., Sharma, D., & Krishna Saha, A. (2018). Phosphate solubilizing capacity and siderophore production by Arthroderma cuniculi Dawson 1963 isolated from rhizospheric soil. Research Journal of Life Sciences, Bioinformatics, Pharmaceutical and Chemical Sciences, 4(3), 330-336. https://doi.org/10.26479/2018.0403.29
Khalid, A., Arshad, M., & Zahir, Z. A. (2004). Screening plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for improving growth and yield of wheat. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 96(3), 473–480. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2003.02161.x
Kumar Bhatt, M., Labanya, R., & Joshi, H. C. (2019). Influence of long-term chemical fertilizers and organic manures on soil fertility - A Review. Universal Journal of Agricultural Research, 7(5), 177–188. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujar.2019.070502
Kumar, A., Patel, J. S., Bahadur, I., & Meena, V. S (Eds.). (2016). Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2776-2
Kunthiphun, S., Wattanagonniyom, T., Endoh, R., Takashima, M., Ohkuma, M., Tanasupawat, S., & Savarajara, A. (2019). Heterocephalacria mucosa sp. nov., a new basidiomycetous yeast species isolated from a mangrove forest in Thailand. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 69(9), 2823–2827. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003562
Kurtzman, C. P., Robnett, C. J., & Blackwell, M. (2016). Description of Teunomyces gen. nov. for the Candida kruisii clade, Suhomyces gen. nov. for the Candida tanzawaensis clade and Suhomyces kilbournensis sp. nov. FEMS Yeast Research, 16(5), article fow041. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/fow041
Lasso, A. M. (2007). Fósforo soluble en agua por el método del ácido ascórbico. Instituto De Hidrología, Meteorología y Estudios Ambientales. http://sgi.ideam.gov.co/documents/412030/97658415/M-S-LC-I020+INSTRUCTIVO+DE+ENSAYO+DETERMINACI%C3%93N++F%C3%93SFORO+SOLUBLE.pdf/11a179cc-828c-4f35-8e31-26fa46d1c631?version=1.0
Limtong, S., Kaewwichian, R., Yongmanitchai, W., & Kawasaki, H. (2014). Diversity of culturable yeasts in phylloplane of sugarcane in Thailand and their capability to produce indole-3-acetic acid. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30, 1785–1796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1602-7
Liu, Y. -Y., Chen, H. -W., & Chou, J. -Y. (2016). Variation in indole-3-acetic acid production by wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae and S. paradoxus strains from diverse ecological sources and its effect on growth. PLOS ONE, 11(8), Article e0160524. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160524
Madden, T. L., Tatusov, R. L., & Zhang, J. (1996). Applications of network BLAST server. Methods in Enzymology, 266, 131-141. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(96)66011-X
Marwanto Bustaman, H., Handajaningsih, M., Supanjani, & Murcitro, B. G. (2021). Qualitative in vitro evaluation of plant growth promoting activity of selected microbial isolates used for biofertilizer application. Proceedings of the International Seminar on Promoting Local Resources for Sustainable Agriculture and Development, 13, 299–309. https://doi.org/10.2991/absr.k.210609.047
Mohamed, H. M., El-Homosy, R. F., Abd-Ellatef, A-E. H., Salh, F. M., & Hussein, M. Y. (2017). Identification of yeast strains isolated from agricultural soils for releasing potassium-bearing minerals. Geomicrobiology Journal, 34(3), 261–266. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2016.1186762
Moreno Quevedo, Á. P., Osorio Vega, N. W., & González Murillo, O. A. (2015). In vitro dissolution of acidulated rock phosphate by phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. Acta Biológica Colombiana, 20(2), 65–71. https://doi.org/10.15446/abc.v20n2.42713
Nakayan, P., Hameed, A., Singh, S., Young, L-S., Hung, M-H., & Young, C-C. (2013). Phosphate-solubilizing soil yeast Meyerozyma guilliermondii CC1 improves maize (Zea mays L.) productivity and minimizes requisite chemical fertilization. Plant and Soil, 373, 301–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1792-z
Nath, D., Ram Maurya, B., & Singh Meena, V. (2017). Documentation of five potassium- and phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria for their K and P-solubilization ability from various minerals. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, 10, 174–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2017.03.007
Nautiyal, C. S. (1999). An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 170(1), 265–270. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13383.x
Nutaratat, P., Srisuk, N., Arunrattiyakorn, P., & Limtong, S. (2014). Plant growth-promoting traits of epiphytic and endophytic yeasts isolated from rice and sugar cane leaves in Thailand. Fungal Biology, 118(8), 683–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2014.04.010
Nutaratat, P., Srisuk, N., Arunrattiyakorn, P., & Limtong, S. (2016). Indole-3-acetic acid biosynthetic pathways in the basidiomycetous yeast Rhodosporidium paludigenum. Archives of Microbiology, 198, 429–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1202-z
Osorno Bedoya, L., & Osorio Vega, N. W. (2017). Evaluación de factores que afectan la bioacidulación de roca fosfórica bajo condiciones in vitro. Revista Colombiana de Biotecnología, 19(1), 53–62. https://doi.org/10.15446/rev.colomb.biote.v19n1.65968
Pandi, R., Velu, G., Devi, P., & Dananjeyan, B. (2019). Isolation and screening of soil yeasts for plant growth promoting traits. Madras Agricultural Journal, 106(7–9), 439–443. https://doi.org/10.29321/MAJ.2019.000289
Peña-Yam, L. P., Ruíz-Sánchez, E., Barboza-Corona, J. E., & Reyes-Ramírez, A. (2016). Isolation of mexican Bacillus species and their effects in promoting growth of chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L. cv Jalapeño). Indian Journal of Microbiology, 56(3), 375–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-016-0582-8
Prabhu, N., Borkar, S., & Garg, S. (2019). Phosphate solubilization by microorganisms. In S. Nandan Meen, & M. Mohan Naik (Eds.), Advances in Biological Science Research (pp. 161–176). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-817497-5.00011-2
Quiñones Ramírez, H., Trejo Cadillo, W., & Juscamaita Morales, J. (2016). Evaluación de la calidad de un abono líquido producido vía fermentación homoláctica de heces de alpaca. Ecología Aplicada, 15(2), 133-142. https://doi.org/10.21704/rea.v15i2.753
Rajawat, M. V. S., Singh, S., Tyagi, S. P., & Saxena, A. K. (2016). A modified plate assay for rapid screening of potassium-solubilizing bacteria. Pedosphere, 26(5), 768–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(15)60080-7
Rawway, M., Ali, S. G., & Badawy, A. S. (2018). Isolation and identification of cellulose degrading bacteria from different Sources at assiut governorate (Upper Egypt). Journal of Ecology of Health & Environment, 6(1), 15–24. https://doi.org/10.18576/jehe/060103
Rojas Contreras, A., Rodríguez Dorantes, A. M., Montes Villafán, S.,Pérez Jiménez, S., Rodríguez Tovar, A., & Guerrero Zúñiga, L. A. (2010). Evaluación de la promoción del crecimiento de Cynodon dactylon L. por rizobacterias productoras de fitohormonas aisladas de un suelo contaminado con hidrocarburos derivados del petróleo. Polibotánica, 29(1), 131–147. https://www.encb.ipn.mx/assets/files/encb/docs/polibotanica/revistas/pb29/cyno.pdf
Samanego Vivanco, T. D. (2018). Determinación de la capacidad de solubilización de potasio por Bacillus mucilaginosus [Tesis de Grado, Universidad Nacional Agraria La Molina]. Repositorio Institucional Universidad Nacional Agraria La Molina. https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12996/3451
Sattar, A., Naveed, M., Ali, M., Zahir, Z. A., Nadeem, S. M., Yaseen, M., Meena, V. S., Farooq, M., Singh, R., Rahman, M., & Meena, H. N. (2019). Perspectives of potassium solubilizing microbes in sustainable food production system: A review. Applied Soil Ecology, 133, 146–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2018.09.012
Sazci, A., Erenler, K., & Radford, A. (1986). Detection of cellulolytic fungi by using Congo red as an indicator: a comparative study with the dinitrosalicyclic acid reagent method. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 61(6), 559–562. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb01729.x
Setiawati, T. C., & Mutmainnah, L. (2016). Solubilization of potassium containing mineral by microorganisms from sugarcane rhizosphere. Agriculture and Agricultural Science Procedia, 9, 108–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaspro.2016.02.134
Sipiczki, M., & Tap, R. M. (2016). Candida vulturna pro tempore sp. nov., a dimorphic yeast species related to the Candida haemulonis species complex isolated from flowers and clinical sample. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 66(10), 4009–4015. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001302
Spadaro, D., & Droby, S. (2016). Development of biocontrol products for postharvest diseases of fruit: The importance of elucidating the mechanisms of action of yeast antagonists. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 47, 39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2015.11.003
Teotia, P., Kumar, V., Kumar, M., Shrivastava, N., & Varma, A. (2016). Rhizosphere Microbes: Potassium Solubilization and Crop Productivity – Present and Future Aspects. In V. S. Meena, B. R. Maurya, J. P. Verma, & R. S. Meena (Eds), Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2776-2
Thais, B. de O., Rodolfo, B. J., Luana, G. S., & Marcia, M. R.-M. (2019). Rhizosphere yeast Torulaspora globosa with plant growth promotion traits and improvement of the development of tomato seedlings under greenhouse conditions. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 14(22), 935–942. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJAR2019.13950
Tzelepis, G., & Karlsson, M. (2019). Killer toxin-like chitinases in filamentous fungi: structure, regulation and potential roles in fungal biology. Fungal Biology Reviews, 33(2), 123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbr.2018.11.001
Ullah, I., Khan, A. R., Park, G-S., Lim, J-H., Waqas, M., Lee, I-J., & Shin, J-H. (2013). Analysis of phytohormones and phosphate solubilization in Photorhabdus spp. Food Science and Biotechnology, 22(S1), 25–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-013-0044-6
Umaña, S., Rodríguez, K., & Rojas, C. (2017). ¿Funcionan realmente los microorganismos de montaña (MM) como estrategia de biofertilización? Un enfoque de ingeniería de biosistemas. Revista de Ciencias Ambientales, 51(2), 133-144. https://doi.org/10.15359/rca.51-2.7
Xiao, C., Chi, R., Pan, X., Liu, F., & He, J. (2013). Rock phosphate solubilization by four yeast strains. Annals of Microbiology, 63(1), 173–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0458-z
You, M., Fang, S., MacDonald, J., Xu, J., & Yuan, Z-C. (2020). Isolation and characterization of Burkholderia cenocepacia CR318, a phosphate solubilizing bacterium promoting corn growth. Microbiological Research, 233, Article 126395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2019.126395
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Marcela Mora-López, Daniel Andrés López-Restrepo, Víctor Manuel Osorio-Echeverri, Liliana Rocío Botero-Botero

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. Proposed policy for open access journals
Authors who publish in this journal accept the following conditions:
a. Authors retain the copyright and assign to the journal the right to the first publication, with the work registered under the attribution, non-commercial and no-derivative license from Creative Commons, which allows third parties to use what has been published as long as they mention the authorship of the work and upon first publication in this journal, the work may not be used for commercial purposes and the publications may not be used to remix, transform or create another work.
b. Authors may enter into additional independent contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the version of the article published in this journal (e.g., including it in an institutional repository or publishing it in a book) provided that they clearly indicate that the work was first published in this journal.
c. Authors are permitted and encouraged to publish their work on the Internet (e.g. on institutional or personal pages) before and during the review and publication process, as it may lead to productive exchanges and faster and wider dissemination of published work (see The Effect of Open Access).