Resumen
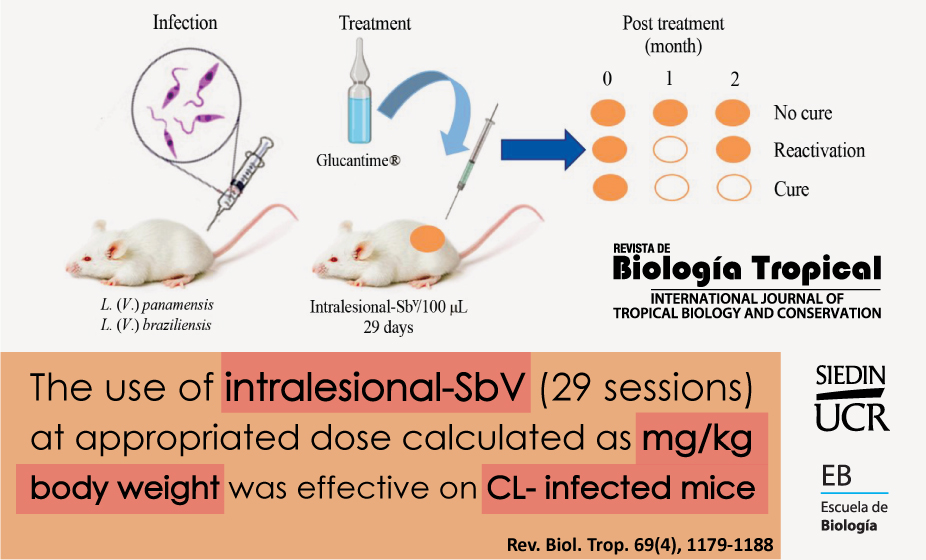
Introducción: Los antimoniales pentavalentes aplicados intralesionalmente (IL-SbV) se recomiendan para el tratamiento de la leishmaniasis cutánea (LC) simple. Se recomiendan pocas sesiones (1-5) y volúmenes (1-5 ml cada uno) en relación con el tamaño de la lesión (LS). No existe un protocolo de IL-SbV validado que utilice dosis calculadas según el peso corporal (en mg/kg) y administradas durante varias sesiones en pocos volúmenes de inyección. Objetivo: El objetivo del estudio fue determinar la eficacia de diferentes concentraciones de IL-SbV administradas en 29 sesiones diarias de 100 μL cada una, en ratones con LC. Métodos: Ratones infectados con L. (V.) panamensis y L. (V.) braziliensis (N = 6) fueron tratados intralesionalmente con 150, 50 y 16,6 mg SbV/kg/día x 29 días. Se determinó el porcentaje de reducción del área de la lesión, la eficacia estética y final (sin lesiones, sin parásitos) y la dosis efectiva (DE)50. Adicionalmente de evaluó la actividad in vitro del SbV. Resultados: Los valores de DE50 fueron 72.2 y 66.3 (al final del tratamiento), 54.3 y 37.7 (15 días pt) y 145.3 y 148.6 (60 días pt) para cada especie. Se encontraron diferencias entre las especies sólo a los 15 días pt. La eficacia del tratamiento IL-SbV-150 mg, 60 días pt., fue de 66.6 y 33.3 % en ratones infectados con L. (V.) panamensis L. (V.) braziliensis respectivamente. Después de 15 días pt., se observó reactivación de la lesión en algunos ratones "estéticamente curados". Glucantime no fue activo in vitro. Conclusiones: El uso intralesional de SbV con una dosis calculada en mg/kg de peso corporal y administrada durante varias sesiones, con pequeños volúmenes de inyección cada día, podría ser eficaz en LC por L. (V.) panamensis y L. (V.) braziliensis. Dosis adecuadas de SbV (superiores a 150 mg/kg/día x 20) deben evaluarse.
##plugins.facebook.comentarios##

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
Derechos de autor 2021 Revista de Biología Tropical