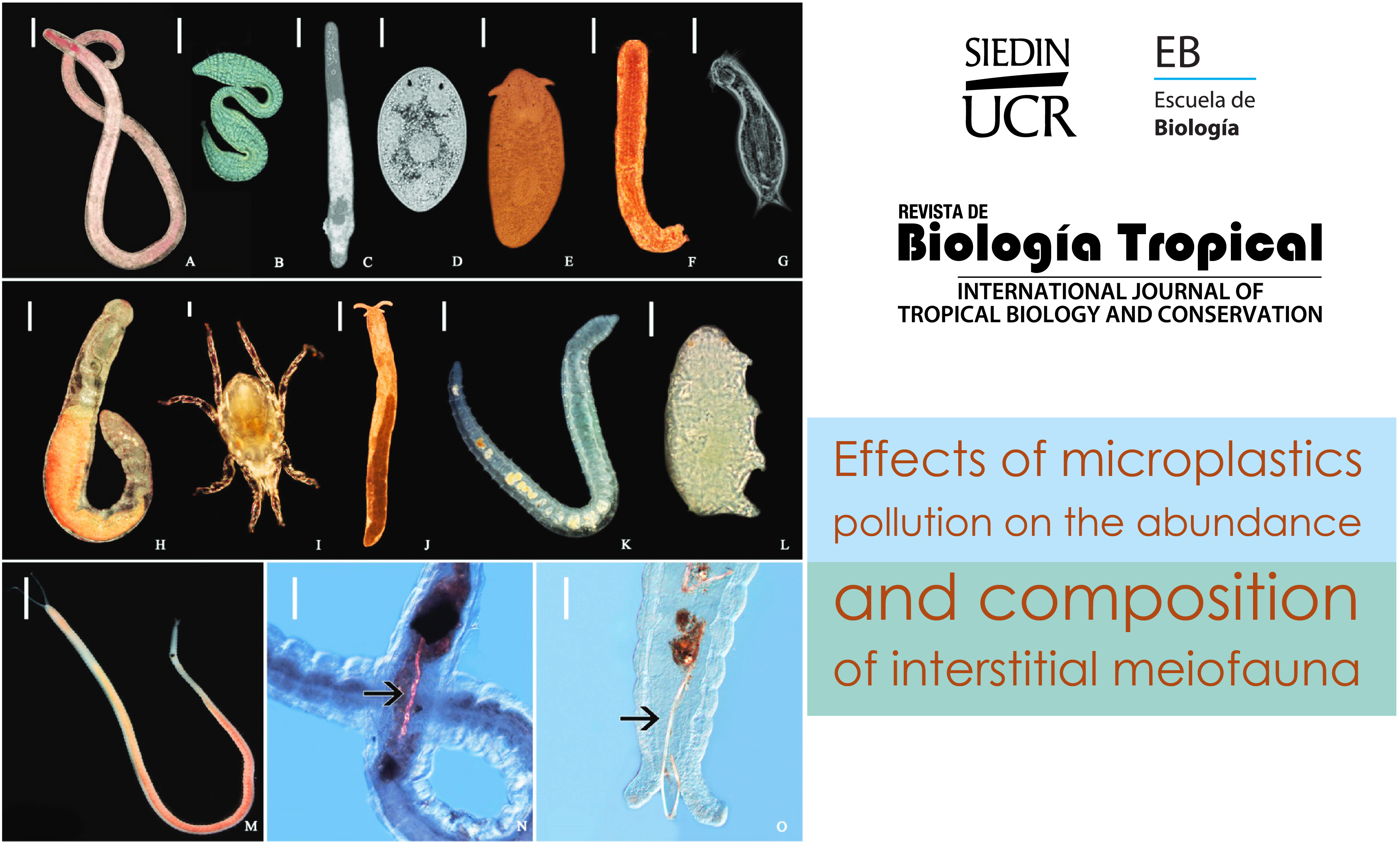
Abstract
Introduction: Pollution by microplastics is a global problem in marine environments, and impacts microorganisms and ecosystems at several spatial levels. Sandy beaches are depositional environments where microplastics tend to accumulate in large quantities. The co-occurrence of interstitial meiofauna and microplastics in sand grains raises the question on whether the accumulation of microplastics in the sediments affects the abundance and composition of the meiofaunal communities. Objective: To test the hypothesis that microplastics affect the meiofauna of urban sandy beaches. Methods: We studied the three main urban sandy beaches of Santa Marta, Colombia: El Rodadero, Santa Marta Bay, and Taganga. All are similar in morphology and external pressures and differ from other beaches in the region. In April 2019 we collected 81 sand samples, equally distributed in the intertidal zone (upper, mid, and lower intertidal levels). We applied generalized linear models to abundance, and multivariate permutational tests to community composition. Results: We identified 17 taxonomic groups of meiofauna, and microplastic particles (mainly 45-500 micron fibres) evenly distributed across beaches and intertidal levels. There was more meiofauna at the mid intertidal level, and in fine and medium grain sediment. At the lower intertidal level, sites with more microplastics had less meiofauna. Microplastics “explained” 39 % of the variation in meiofaunal communities at lower intertidal levels. Conclusions: The accumulation of microplastics has a negative impact on these meiofaunal interstitial communities. This is not surprising: microplastics occupy the same physical space as these animals, presumably modifying the structure of sediments and the composition of interstitial water.
Objective: As a step forward on that direction, we have here analysed the distribution of the abundance of microdebris and major interstitial meiofaunal groups in three urban sandy beaches in Santa Marta region, Colombia, and possible relation among both factors.
Methods: We selected the three main urban sandy beaches in Santa Marta, Northern Colombia: El Rodadero, Bahía de Santa Marta, and Taganga. All of them are very similar to each other due to its morfolophy and extern pressions, and differ starkly from other beaches in the region. Sampling was performed in April 2019 with a 81 samples in total equitably distributed in the supratidal zone, intertidal zone, and subtidal zone. In each point, we collected samples for microplastics quantification, meiofaunal community characterization, and granulometric analysis.
Results: We extracted a total of 1131 debris particles, dominated by fibres ranging between 45-500 microns. Generalised linear models showed that microdebris were uniformly distributed across beaches and tidal levels, whereas meiofaunal abundances were significantly affected by the granulometry and tidal level. We detected a significant correlation between the abundance of microplastics and meiofauna at those levels, although with a very small estimate. Furthermore, our permutational multivariate tests showed that the abundance of microdebris significantly explained the 39.3% of the variation of the meiofaunal communities at the lowest tidal levels.
Conclusions: Our result suggested that microdebris accumulating amongst the beach sand grains negatively impact meiofaunal diversity. This is not surprising, given that microdebris occupy the same physical space than these animals, presumably modifying the structure of the sediments and the composition of the interstitial water.
References
Acosta-Coley, I., Mendez-Cuadro, D., Rodríguez-Cavallo, E., de la Rosa, J., & Olivero-Verbel, J. (2019). Trace elements in microplastics in Cartagena: a hotspot for plastic pollution at the Caribbean. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 139, 402–411.
Acosta-Coley, I., & Olivero-Verbel, J. (2015). Microplastic resin pellets on an urban tropical beach in Colombia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4602-7
Alexeev, D. K., & Galtsova, V. V. (2012). Effect of radioactive pollution on the biodiversity of marine benthic ecosystems of the Russian Arctic shelf. Polar Science, 6, 183–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polar.2012.04.001
Alves, A. S., Caetano, A., Costa, J. L., Costa, M. J., & Marques, J. C. (2015). Estuarine intertidal meiofauna and nematode communities as indicators of ecosystem recovery following mitigation measures. Ecological Indicators, 54, 184–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.02.013
Altamar, J., Correa-Helbrum, J., Restrepo-Leal, D., & Robles-Algarín, C. (2020). Reconstructed data of landings for the artisanal beach seine fishery in the marine-coastal area of Taganga, Colombian Caribbean Sea. Data in Brief, 30, 105604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2020.105604
Alomar, C., Estarellas, F., & Deudero, S. (2016). Microplastics in the Mediterranean Sea: Deposition in coastal shallow sediments, spatial variation and preferential grain size. Marine Environmental Research, 115, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2016.01.005
Ape, F., Sará, G., Airoldi, L., Mancuso, F., & Mirto, S. (2017). Influence of environmental factors and biogenic habitats on intertidal meiofauna. Hydrobiologia, 807, 349–366. https://doi.org/10.1007%2Fs10750-017-3410-1
Álvarez-Zeferino, J., Ojeda-Benítez, S., Cruz-Salas, A. A., Martínez-Salvador, C., & Vázquez-Morillas, A. (2020). Microplastics in Mexican beaches. Resources, Conservation & Recycling, 1551, 104633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104633
Buchanan, J. B. (1984). Sediment analysis. In N. A., Holme, & A. D. McIntyre (Eds.), Methods for the Study of Marine Benthos (pp. 41–63). Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Browne, M. A., Crump, P., Niven, S. J., Teuten, E. L., Tonkin, A., Galloway, T., & Thompson, R. C. (2011). Accumulations of microplastic on shorelines worldwide: sources and sinks. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 9175−9179. https://doi.org/10.1021/es201811s
Bezerra, T. N. C., Genevois, B., & Fonsêca-Genevois, V. (1997). Influência da granulometria na distribuição e adaptação da meiofauna na praia arenosa do Istmo de Olinda PE. In S. A. Silva, P. A. Grohmann & A. M. Esteves (Eds.), Ecologia de Praias Arenosas do Litoral Brasileiro (pp. 107–116). Programa de Pós-Graduação em Ecologia da UFRJ.
Baia, E., & Venekey, V. (2019). Distribution patterns of meiofauna on a tropical macrotidal sandy beach, with special focus on nematodes (Caixa d’Água, Amazon Coast, Brazil). Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 67, e19230. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1679-87592019023006701
Botero, C. M., & Zienliski, S. (2020). The implementation of a world-famous tourism ecolabel triggers political support for beach management. Tour Management Perspectives, 35, 100691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmp.2020.100691
Curini-Galletti, M., Artois, T., Delogu, V., De Smet, W. H., Fontaneto, D., Jondelius, U., Leasi, F., Martínez, A., Meyer-Wachsmuth, I., Nilsson, K. S., Tongiorgi, P., Worsaae, K., & Todaro, M. A. (2012). Patterns of Diversity in Soft-Bodied Meiofauna: Dispersal Ability and Body Size Matte. PLoS One, 7, e33801. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033801
Carson, H. S., Colbert, S. L., Kaylor, M. J., & McDermid, K. J. (2011). Small plastic debris changes water movement and heat transfer through beach sediments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62, 1708–1713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.032
Claessens, M., De Meester, S., Van Landuyt, L., De Clerck, K., & Janssen, C. R. (2011). Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in marine sediments along the Belgian coast. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62, 2199–2204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.06.030
Coley, R., Hardiman, G., & O’Driscolla, K. (2020). Microplastics in the marine environment: A review of their sources, distribution processes, uptake and exchange in ecosystems. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 2, 100010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2020.100010
Cannon, S. M. E., Lavers, J., & Figueireda, B. (2016). Plastic ingestion by fish in the southern hemisphere: a baseline study and review of methods. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 107, 286–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.03.057
Cole, M., Lindeque, P. K., Fileman, E. S., Halsband, C., Goodhead, R., Moger, J., & Galloway, T. S. (2013). Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environmental Science & Technology, 47, 6646–6655. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400663f
Cole, M., Lindeque, P., Halsband, C., & Galloway, T. S. (2011). Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: a review. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62, 2588–2597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.09.025
Correa, I., & Morton, R. (2010). Caribbean Coast of Colombia. In E.C. F. Bird (Ed.), Encyclopedia of the World's Coastal Landforms (pp. 259–264). Springer.
Castro, L. R., Meyer, R. S., Shapiro, B., Shirazi, S., Cutler, S., Lagos, A. M., & Quiroga, S. Y. (2021). Metabarcoding meiofauna biodiversity assessment in four beaches of Northern Colombia: effects of sampling protocols and primer choice. Hydrobiologia, 848, 3407–3426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-021-04576-z
Derraik, J. G. B. (2002). The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: a review. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44, 842–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00220-5
Desforges, J. P. W., Galbraith, M., & Ross, P. S. (2015). Ingestion of microplastics by zooplankton in the northeast Pacific Ocean. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 69, 320–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-015-0172-5
Defeo, O., & McLachlan, A. (2005). Patterns, processes and regulatory mechanisms in sandy beach macrofauna: a multiscale analysis. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 295, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps295001
Di, M., & Wang, J. (2018). Microplastic in surface waters and sediments of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Science of the Total Environment, 616, 1620–1627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.150
Faraday, S. (2019). Microplastics as a new, ubiquitous pollutant: Strategies to anticipate management and advise seafood consumers. Marine Policy, 104, 103–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2019.02.020
Fossi, M. C., Coppola, D., Baini, M., Giannetti, M., Guerranti, C., Marsili, L., Panti, C., de Sabata, E., & Clo, S. (2014). Large filter feeding marine organisms as indicators of microplastic in the pelagic environment: the case studies of the Mediterranean basking shark (Cetorhinus maximus) and fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus). Marine Environmental Research, 100, 17-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2014.02.002
Fanini, L., Defeo, O., & Elliott, M. (2020). Advances in sandy beach research – Local and global perspectives. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 234, 106646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106646
Fonseca, G., Norenburg, J., & Di Domenico, M. (2014). Diversity of marine meiofauna on the coast of Brazil. Marine Biodiversity, 44, 459–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-014-0261-0
Folk, R. L., & Ward, W. C. (1957). A study in the significance of grain-size parameters. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 27, 3–26. https://doi.org/10.1306/74D70646-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Fueser, H., Mueller, M. T., & Traunspurger, W. (2020). Ingestion of microplastics by meiobenthic communities in small-scale microcosm experiments. Science of the Total Environment, 746, 141276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141276
Fueser, H., Mueller, M. T., Weiss, L., Höss, S., & Traunspurger, W. (2019). Ingestion of microplastics by nematodes depends on feeding strategy and buccal cavity size. Environmental Pollution, 255, 113227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113227
Fuentes-Reines, J. M., Suárez-Morales, E., & Eslava-Eljaiek, P. (2021). Occurrence of Notodiaptomus maracaibensis Kiefer, 1954 (Copepoda, Calanoida, Diaptomidae) from an ephemeral pond in northern Colombia. Intropica, 16(2), 125–132. https://doi.org/10.21676/23897864.3977
Giere, O. (2009). Meiobenthology: The microscopic motile fauna of aquatic sediments (2nd ed.). Springer-Verlag.
Giere, O. (2019). Future trend lines in ecological meiobenthos research. In O. Giere (Ed.), Perspectives in Meiobenthology Reviews, Reflections and Conclusions (pp. 37–49). Springer-Verlag.
González-Cueto, J., Quiroga, S., & Norenburg, J. (2014). A shore-based preliminary survey of marine ribbon worms (Nemertea) from the Caribbean coast of Colombia. ZooKeys, 439, 83–108. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.439.5965
Gusmão, F., Domenico, M. D., Amaral, A. C. Z., Martínez, A., Gonzalez, B. C., Worsaae, K., do Sul, J. A. I., & da Cunha-Lana, P. (2016). In situ ingestion of microfibres by meiofauna from sandy beaches. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 216, 584-590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.06.015
Garcés-Ordóñez, O., Espinosa, L., Pereira, R., Barroso, B., & Meigikos, R. (2020b). Plastic litter pollution along sandy beaches in the Caribbean and Pacific coast of Colombia. Environmental Pollution, 267, 115495.
Garcés-Ordóñez, O., Espinosa, L., Pereira, R., & Costa, M. (2020a). The impact of tourism on marine litter pollution on Santa Marta beaches, Colombian Caribbean. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 160, 111558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111558
García, F., Palacio, C., & García, U. (2011). Constituyentes de marea en la bahía de Santa Marta (Colombia). Dyna, 78, 142–150.
Gheskiere, T., Vincx, M., Weslawski, J. M., Scapini, F., & Degraer, S. (2005). Meiofauna as descriptor of tourism-induced changes at sandy beaches. Marine Environmental Research, 60, 245–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2004.10.006
Haegerbaeumer, A., Mueller, M. T., Fueser, H., & Traunspurger, W. (2019). Impacts of micro- and nano-sized plastic particles on benthic invertebrates: A literature review and gap analysis. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 7, 1–33. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2019.00017
Hourston, M., Warwick, R. M., Valesini, F. J., & Potter, I. C. (2005). To what extent are the characteristics of nematode assemblages in nearshore sediments on the west Australian coast related to habitat type, season and zone? Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 64, 601–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2005.04.001
Hidalgo-Ruz, V., Gutow. L., Thompson, R. C., & Thiel, M. (2012). Microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environmental Science & Technology, 46, 3060–3075. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2031505
de Jonge, V. N., & Bouwman, L. A. (1977). A simple density Kennedy: A rapid-freezing method separation technique for quantitative isolation of meiobenthos using the colloidal silica Ludox-TM. Marine Biology, 42, 143–148.
Kutralam-Muniasamy, G., Pérez-Guevara, F., Elizalde-Martínez, I., & Shruti, V. C. (2020). Review of current trends, advances and analytical challenges for microplastics contamination in Latin America. Environmental Pollution, 267, 115463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115463
Lagos, A. M. (2018). Meiofauna intermareal de la región de Santa Marta (Tesis de Maestría). Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Colombia.
Lusher, A. (2015). Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Distribution, Interactions and Effects, In M. Bergmann, L. Gutow, & M. Klages (Eds.), Marine Anthropogenic Litter (pp. 245–307). Springer International Publishing.
Lots, F. A. E., Behrens, P., Vijver, M. G., Horton, A. A., & Bosker, T. (2017). A large-scale investigation of microplastic contamination: Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in European beach sediment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 123, 219-226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.08.057
Liebezeit, G., & Dubaish, F. (2012). Microplastics in beaches of the East Frisian islands Spiekeroog and Kachelotplate. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 89, 213-217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0642-7
Li, H. X., Getzinger, G. J., Ferguson, P. L., Orihuela, B., Zhu, M., & Rittschof, D. (2016). Effects of toxic leachate from commercial plastics on larval survival and settlement of the barnacle Amphibalanus amphitrite. Environmental Science & Technology, 5, 924–931. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b02781
Lagos, A. M., Leon, M. V., Quiroga, S., & Martínez, A. (2018). Interstitial annelids from the Caribbean coast of Colombia. Revista de Biología Tropical, 66, 658-673. http://doi.org/10.15517/rbt.v66i2.33399
Liñero-Arana, I., Ojeda, S., & Amaro, M. E. (2012). Variación espacio-temporal de la meiofauna submareal en una playa arenosa nororiental de Venezuela. Revista de Biología Tropical, 61, 59-73.
Leasi, F., Sevigny, J. L., Laflamme, E. M., Artois, T., Curini-Galletti, M., Navarrete, A., Di Domenico, M., Goetz, F., Hall, J. A., Hochberg, R., Jörger, K. M., Jondelius, U., Todaro, M. A., Wirshing, H. H., Norenburg, L. J., & Thomas, W. K. (2018). Biodiversity estimates and ecological interpretations of meiofaunal communities are biased by the taxonomic approach. Communications Biology, 1, 1-12. http://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-018-0119-2
Lu, K., Qiao, R., An, H., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Influence of microplastics on the accumulation and chronic toxic effects of cadmium in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere, 202, 514–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.145
Mathalon, A., & Hill, P. (2014). Microplastic fibers in the intertidal ecosystem sur- rounding Halifax Harbor, Nova Scotia. Marine Polluttion Bulletin, 81, 69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.02.018
McLachlan, A., & Brown, A. C. (2006). The ecology of sandy shores. Academic Press.
Martínez, A., Di Domenic, M., Leasi, F., Curini-Galletti, M., Todaro, M. A., Dal Zotto, M., Gobert, S., Artois, T., Norenburg, J., Jörger, K., Núñez, J., Fontaneto, D., & Worsaae, K. (2019). Patterns of diversity of soft-bodied meiofauna in an oceanic island, Lanzarote (Canary Islands). Marine Biodiversity, 49, 2033–2055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-019-01007-0
Martínez, A., Eckert, E. M., Artois, T., Careddu, G., Casu, M., Curini-Galletti, M., Gazale, V., Gobert, S., Ivanenko, V. N., Jondelius, U., Marzano, M., Pesole, G., Zanello, A., Todaro, M. A., & Fontaneto, D. (2020). Human access impacts biodiversity of microscopic animals in sandy beaches. Communications Biology, 3, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-0912-6
Mueller, M. T., Fueser, H., Höss, S., & Traunspurger, W. (2020). Species-specific effects of long-term microplastic exposure on the population growth of nematodes, with a focus on microplastic ingestion. Ecological Indicators, 118, 106698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106698
Mancera-Pineda, J. E. M., Pinto, G., & Vilardy, S. (2013). Patrones de distribución estacional de masas de agua en la bahía de Santa Marta, Caribe colombiano: importancia relativa del upwelling y outwelling. Bulletin of Marine and Coastal Research, 2, 329–360. https://doi.org/10.25268/bimc.invemar.2013.42.2.55
MSFD-TSGML. (2013). Guidance on monitoring of marine litter in European Seas: a guidance document within the common implementation strategy for the marine strategy framework directive. EUR-26113 EN. JRC Scientific and Policy Reports JRC83985. https://mcc.jrc.ec.europa.eu/documents/201702074014.pdf
Nadal, M. A., Alomar, C., & Deudero, S. (2016). High levels of microplastic ingestion by the semipelagic fish Bogue Boops boops (L.) around the Balearic Islands. Environmental Pollution, 214, 517–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.054
Nor, N. H. M., & Obbard, J. (2014). Microplastics in Singapore's coastal mangrove ecosystem. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 79, 278–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.11.025
Oksanen, J., Blanchet, F. G., Friendly, M., Kindt, R., Legendre, P., McGlinn, D., Minchin, P. R., O’Hara, R. B., Simpson, G. L., Solymos, P., Stevens, M. H. H., Szoecs, E., & WagnerVegan, H. (2018). Community Ecology Package. R package version 2, 5–2. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Ogonowski, M., Schür, C., Jarsén, Å., & Gorokhova, E. (2016). The effects of natural and anthropogenic microparticles on individual fitness in Daphnia magna. PLoS One, 11, e0155063. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155063
Pereira, T. J., Gingold, R., Villegas, A. D. M., & Rocha-Olivares, A. (2018). Patterns of spatial variation of meiofauna in sandy beaches of Northwestern Mexico with contrasting levels of disturbance. Thalassas, 34, 53–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-017-0038-x
Piperagkas, O., Papageorgiou, N., & Karakassis, I. (2019). Qualitative and quantitative assessment of microplastics in three sandy Mediterranean beaches, including different methodological approaches. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 219, 169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2019.02.016
Portz, L., Portantiolo-Manzolli, R., Vasquez-Herrera, G., Laiton-Garcia, L., Villate, D. A., & do Sul, J. A. I. (2020). Marine litter arrived: Distribution and potential sources on an unpopulated atoll in the Seaflower Biosphere Reserve, Caribbean Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 157, 111323.
Peng, G., Zhu, B., Yang, D., Su, L., Shi, L., & Li, D. (2017). Microplastic in sediments of the Changjaiang Estuary, China. Environmental Pollution, 225, 283–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.064
R Core Team. (2016). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Rodríguez, J. G. (2004). Community structure of intertidal meiofauna along a gradient of morphodynamic states on an exposed North Sea beach. Sarsia, 89, 22–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/00364820310003307
Rochman, C. M., Hoh, E., Kurobe, T., & The, S. J. (2013). Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress. Scientific Reports, 3, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03263
Rodríguez, J. G., López, J., & Jaramillo, E. (2001). Community structure of the intertidal meiofauna along a gradient of morphodynamic sandy beach types in southern Chile. Revista Chilena de Historia Natural, 74, 885–897.
Rangel-Buitrago, N. G., Anfuso, G., & Williams, A. T. (2015). Coastal erosion along the Caribbean coast of Colombia: magnitudes, causes and management. Ocean & Coastal Management, 114, 129–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2015.06.024
Rangel-Buitrago, N. G., Ruiz, A. G., & López, N. T. (2019). Grain–size analysis and characterization of sedimentary environments of the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta (SNSM) coastal zone, caribbean of Colombia. Revista ITTPA, 1, 13–19.
Rubio-Polanía, J. C., & Trujillo-Arcila, C. A. (2013). Características granulométricas de los fondos blandos en un área de la bahía de Taganga (Colombia) influenciada por la instalación de refugios bentónicos. Revista U.D.C.A, 16, 193-203. https://doi.org/10.31910/rudca.v16.n1.2013.875
Somerfield, P. (2008). Identification of the Bray-Curtis similarity index: Comment on Yoshioka (2008). Marine Ecology Progress Series, 372, 303-306. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps07841
Sevilla-Hernández, M. (2016). Ácaros marinos (Arachnida: Acari) asociados al alga Ulva lactuca de la bahía de Taganga (Santa Marta, Colombia) (Tesis de Bachillerato). Universidad del Magdalena, Colombia.
Setälä, O., Fleming-Lehtinen, V., & Lehtiniemi, M. (2014). Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environmental Pollution, 185, 77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.10.013
Strungaru, S. A., Jijie, R., Nicoara, M., Plavan, G., & Faggio, C. (2019) Micro- (nano) plastics in freshwater ecosystems: abundance, toxicological impact and quantification methodology. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 110, 116–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.10.025
Talvitie, J., Heinonen, M., Pääkkönen, J. P., Vahtera, E., Mikola, A., Setälä, O., & Vahala, R. (2015). Do wastewater treatment plants act as a potential point source of microplastics? Preliminary study in the coastal Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Water Science & Technology, 72, 1495–1504. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.360
Tsang, Y. Y., Mak, C. W., Liebich, C., Lam, S. W., Sze, E. T., & Chan, K. M. (2017). Microplastic pollution in the maine eater and sediments of Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 115, 20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.11.003
Thompson, R. C., Olsen, Y., Mitchell, R. P., Davis, A., Rowland, S. J., John, A. W. G., McGonigle, D., & Russell, A. E. (2004). Lost at sea: where is all the plastic? Science, 304, 838.
Van Cauwenberghe, L., Claessens, M., Vandegehuchte, M. B., & Janssen, C. R. (2015). Microplastics are taken up by mussels (Mytilus edulis) and lugworms (Arenicola marina) living in natural habitats. Environmental Pollution, 199, 10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.008
Van Cauwenberghe, L., Vanreusel, A., Mees, J., Janssen, C. R. (2013). Microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments. Environmental Pollution, 182, 495–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.08.013
Von Moos, N., Burkhardt-Holm, P., & Koehler, A. (2012). Uptake and effects of microplastics on cells and tissue of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis L. after an experimental exposure. Environmental Science & Technology, 46, 327–335. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302332w
Wakkaf, T., Allouche, M., Harrath, A. H., Mansour, L., Alwasel, S., Thameemul-Ansari, K. G. M., Beyrem, H., Sellami, B., & Boufahja, F. (2020). The individual and combined effects of cadmium, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) microplastics and their polyalkylamines modified forms on meiobenthic features in a microcosm. Environmental Pollution, 266, 115263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115263
Wesch, C., Bredimus, K., Paulus, M., & Klein, R. (2016) Towards the suitable monitoring of ingestion of microplastics by marine biota: a review. Environmental Pollution, 218, 1200-1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.076
Wright, L. D., Chappell, J., Thom, B. G., Bradshaw, M. P., & Cowell, P. (1979). Morphodynamics of reflective and dissipative beach and inshore systems: southeastern Australia. Marine Geology, 32, 105–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-3227(79)90149-X
Willis, K. A., Eriksen, R., Wilcox, C., & Hardesty, B. D. (2017). Microplastic distribution at different sediment depths in an urban estuary. Frontiers in Marine Science, 4, 419. https:/doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2017.00419
Wang, T., Hu, M., Song, L., Yu, J., Liu, R., Wang, S., Wang, Z., Sokolova, I. M., Huang, W., & Wang, Y. (2020). Coastal zone use influences the spatial distribution of microplastics in Hangzhou Bay, China. Environmental Pollution, 266, 115137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115137
Wright, S. L., Rowe, D., Thompson, R. C., & Galloway, T. S. (2013). Microplastic ingestion decreases energy reserves in marine worms. Current Biology, 23, R1031-R1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.10.068
Wright, L. D., & Short, A. D. (1984). Morphodynamic variability of surf zones and beaches: a synthesis. Marine Geology, 56, 93–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-3227(84)90008-2
Zubris, K. A. V., & Richards, B. K. (2005). Synthetic fibers as an indicator of land application of sludge. Environmental Pollution, 138, 201–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.04.013
Zeppilli, D., Sarrazin, J., Leduc, D., Martinéz-Arbizu, P., Fontaneto, D., Fontanier, C., Gooday, A. J., Kristensen, R. M., Ivanenko, V. N., Sørensen, M. V., Vanreusel, A., Thébault, J., Mea, M., Allio, N., Andro, T., Arvigo, A., Castrec, J., Danielo, M., Foulon, V., Fumeron, R., Hermabessiere, L., Hulot, V., James, T., Langonne-Augen, R., Le Bot, T., Long, M., Mahabror, D., Morel, Q., Pantalos, M., Pouplard, E., Raimondeau, L., Rio-Cabello, A., Seite, S., Traisnel, G., Urvoy, K., Van Der Stegen, T., Weyand, M., & Fernandes, D. (2015). Is the meiofauna a good indicator for climate change and anthropogenic impact. Marine Biodiversity, 45, 505–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-015-0359-z
Zhu, L., Wang, H., Chen, B., Sun, X., Qu, K., & Xia, B. (2019). Microplastic ingestion in deep-sea fish from the South China Sea. Science of the Total Environment, 677, 493–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.380
##plugins.facebook.comentarios##

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright (c) 2023 Revista de Biología Tropical