Calidad microbiológica y fisicoquímica y sabor de huevos de gallina de producción convencional o pastoreo
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15517/am.v33i1.46140Palabras clave:
Escherichia coli, Salmonella sp., Isa Brown, unidades Haugh, prueba tétradaResumen
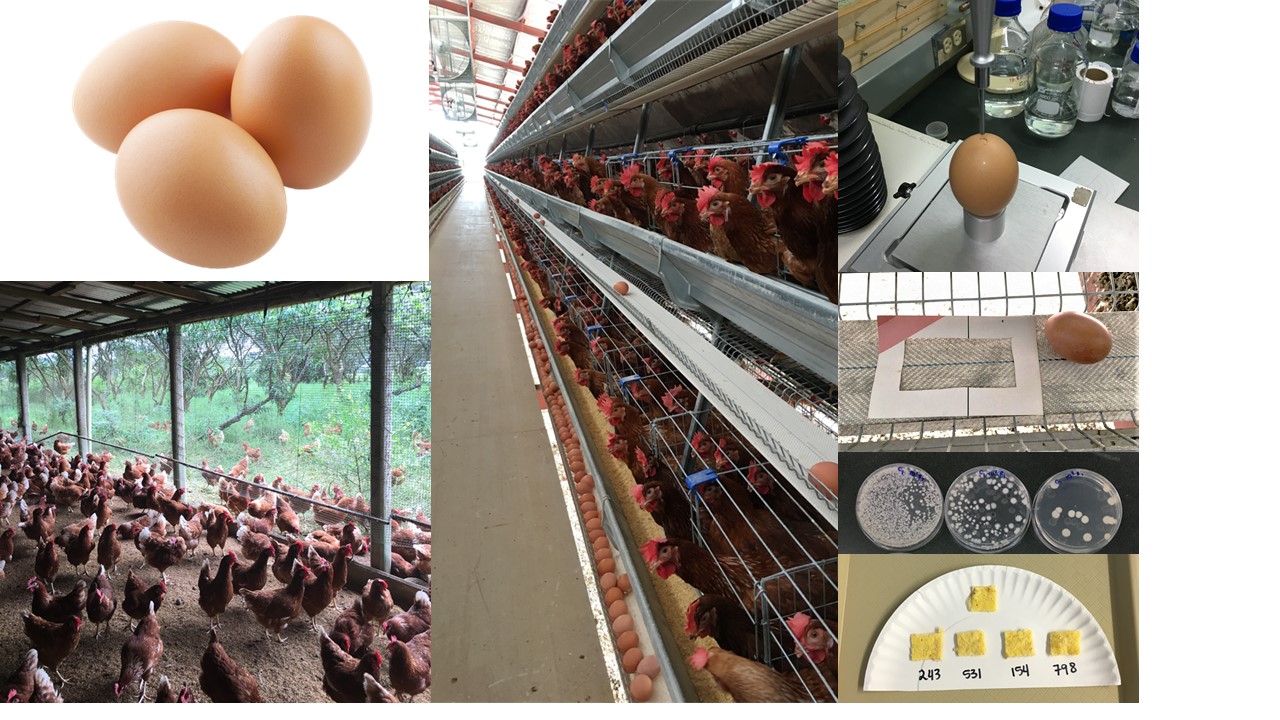
Introducción. El huevo de gallina (Gallus gallus domesticus) es un alimento nutritivo de la dieta de millones de personas. Su producción mundial se obtiene con el empleo de jaulas convencionales, aunque existen sistemas alternativos como el pastoreo. Objetivo. Comparar la calidad microbiológica, fisicoquímica y el sabor de huevos provenientes de granjas con sistemas productivos convencionales o de pastoreo en Costa Rica. Materiales y métodos. El trabajo se realizó en Alajuela, Costa Rica de octubre del 2016 a mayo del 2017. Se muestrearon superficies y huevos de gallinas Isa Brown en granjas con sistemas productivos convencionales o de pastoreo y se determinó el recuento de coliformes totales, Escherichia coli, mohos y levaduras y ausencia/presencia de Salmonella sp. Además, se analizaron parámetros fisicoquímicos (unidades Haugh, índice de yema, pH, color de yema y dureza de cáscara) y se realizó una prueba sensorial de discriminación con consumidores. Resultados. Los sistemas de producción de pastoreo tienen superficies en contacto con los huevos con recuentos de coliformes totales y E. coli significativamente mayores que las superficies del sistema convencional. Los huevos de pastoreo presentaron recuentos de coliformes totales (3,2 log10 UFC huevo-1) significativamente mayores que los huevos convencionales (2,3 log10 UFC huevo-1). Salmonella sp. estuvo presente en 8 % de las muestras de pastoreo (incidencia no diferente de 0) y ausente en las convencionales. Se encontró diferencia en el color de la yema (más oscura en los huevos convencionales). Además, hubo diferencia significativa en el sabor de ambos tipos de huevo. Conclusión. En general, existió diferencia en la calidad microbiológica, fisicoquímica y el sabor de huevos producidos en granja de tipo convencional o pastoreo.
Descargas
Citas
Arbona, D. V. (2011). A comparative analysis of freerange vs caged layer hens: egg productivity and quality, humoral immunocompetency & follicular expression of glucocorticoid receptors [Master´s Thesis, North Carolina State University], North California State University libraries. http://www.lib.ncsu.edu/resolver/1840.16/6955
Association of Official Agricultural Chemists. (2005a). AOAC official method 981.12 pH of acidified foods. http://www.eoma.aoac.org/methods/info.asp?ID=18372
Association of Official Agricultural Chemists. (2005b). AOAC official method of analysis 991, 14 coliform and Escherichia coli counts in foods. http://www.eoma.aoac.org/methods/info.asp?ID=46949
Bovšková, H., Míková, K., &, Panovská Z. (2014). Evaluation of egg yolk color. Czech Journal Of Food Science, 32, 213–217. https://doi.org/10.17221/47/2013-CJFS
Bray, H. J., & Ankeny, R.A. (2017) Happy chickens lay tastier eggs: motivations for buying free-range eggs in Australia. Anthrozoös, 30(2), 213–226. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927936.2017.1310986
Caner, C., & Yuceer, M. (2015). Efficacy of various protein-based coating on enhancing the shelf life of fresh eggs during storage. Poultry Science, 94, 1665–1677. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pev102
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2011). National enteric disease surveillance: Salmonella surveillance overview. http://www.cdc.gov/nationalsurveillance/PDFs/NationalSalmSurveillOverview_508/
Central America Data. (2014). Crece la demanda de huevos en Costa Rica. http://www.centralamericadata.com/es/article/home
Clerici, F., Casiraghi, E., Hidalgo, A., & Rossi, M. (2006, September 10-14). Evaluation of eggshell quality characteristics in relation to the housing system of laying hens [Conference presentation]. European Poultry Conference 2006, Verona, Italy.
Coutts, J. A., & Wilson, G. C. (Eds.). (2007). Optimum egg quality: a practical approach. 5M Publishing.
De Reu, K. (2006). Bacteriological contamination and infection of shell eggs in the production chain [Doctoral dissertation, University of Ghent]. CORE open. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/55719222.pdf
De Reu, K., Messens, W., Heyndrlckx, M., Rodenburg, B., Uyttendaele, M., & Herman, L. (2008). Bacterial contamination of hen’s table eggs and its influencing by housing systems. World’s Poultry Science Journal, 64(1), 5–19. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0043933907001687
De Reu, K., Rodenburg, T. B., Grijspeerdt, K., Messens, W., Heyndrickx, M., Tuyttens, F. A. M., Sonck, B., Zoons, J., & Herman, L. (2009). Bacteriological contamination, dirt, and cracks of eggshells in furnished cages and noncage systems for laying hens: An international on-farm comparison. Poultry Science, 88, 2442–2448. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2009-00097
Eke, M. O., Olaitan, N. I., & Ochefu, J. H. (2013). Effect of storage conditions on the quality attributes of shell table eggs. Nigerian Food Journal, 31(2), 18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0189-7241(15)30072-2
Englmaierová, M., Tumova, E., Charvatova, V., & Skrivan, M. (2014). Effects of laying hens housing system on laying performance, egg quality characteristics and egg microbial contamination. Czech Journal of Animal Science, 59(8), 345–352. https://doi.org/10.17221/7585-CJAS
Ennis, J. M., & Jesionka, V. (2011). The power of sensory discrimination methods revisited. Journal of Sensory Studies, 26, 371–382. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-459X.2011.00353.x
Fischer, J. (2010). Influence of housing system on bacterial eggshell contamination and horizontal transmission of Salmonella and Campylobacter among laying hens [Doctoral dissertation, University of Georgia]. University of Georgia Libraries. https://getd.libs.uga.edu/pdfs/hannah_jackie_f_201012_phd.pdf
Food and Drug Administration. (2018). Bacteriological Analytical Manual. https://www.fda.gov/food/laboratory-methods-food/bacteriological-analytical-manual-bam
Food Standards Australia New Zealand. (2016). Compendium of Microbiological Criteria for Food. Food Standards Australia New Zealand Publishing. https://www.foodstandards.gov.au/publications/Documents/Compedium%20of%20Microbiological%20Criteria/Compendium_revised-Sep%202018.pdf
Fronding, G. W. (1998, June 2–3). Egg processing: ideas for the future [Conference Presentation]. Egg Processing Workshop, California, United States. https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/read/19008238/egg-processing-ideas-for-the-future-glenn-froning
Giacomozzi, J. (2014). Situación actual de la industria del huevo. Oficina de estudios y políticas agrarias de Chile. https://www.odepa.gob.cl/publicaciones/articulos/situacion-actual-de-la-industria-del-huevo-junio-de-2014
Gjorgovska, N., Filev, K., & Levov, V. (2011). External and internal quality of eggs produced from aged hens. Lucrari Stiintifice, 56, 342–345.
Greco, M. V., Franchi, M. L., Rico S. L., Pardo, A. G., & Pose, G. N. (2014). Mycotoxins and mycotoxigenic fungi in poultry feed for food-producing animals. The Scientific World Journal, 2014, Article 968215. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/968215
Hannah, J. F., Wilson, J. L., Cox, N. A., Cason, J. A., Bourassa, D. V., Musgrove, M. T., Richardson, L. J., Rigsby, L. L., & Buhr, R. J. (2011). Comparison of shell bacteria from unwashed and washed table eggs harvested from caged laying hens and cage-free floor-housed laying hens. Poultry Science, 90, 1586–1593. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2010-01115
Holt, P. S., Davies, R. H., Dewulf, J., Gast, R. K., Huwe, J. K., Jones, D. R., Waltman D., & Willian, K. R. (2011). The impact of different housing systems on egg safety and quality. Poultry Science, 90, 251–262. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2010-00794
Hui, Y. H. (2014). Plant sanitation for food processing and food service (2nd Ed.). CRC Press.
Jaramillo, A. H., Mogica, J., Caro, E. A., & Sosa, J. (2018). Evaluación de la calidad del huevo de gallina en dos sistemas de alojamiento –piso convencional con suplementación de sauco (Sambucus nigra) y pastoreo con kikuyo (Pennisetum clandestinum)– en la Sabana de Bogotá. Revista Siembra CBA, 2(1), 59–77. http://revistas.sena.edu.co/index.php/Revsiembracba/article/view/1881/1987
Jones, D. R., & Anderson, K. E. (2013). Housing system and laying hen strain impacts on egg microbiology. Poultry Science, 92, 2221–2225. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2012-02799
Jones, D. R., Anderson, K. E., & Guard, J. Y. (2012). Prevalence of coliforms, Salmonella, Listeria and Campylobacter associated with eggs and the environment of conventional cage and free-range egg production. Poultry Science, 91, 1195–1202. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2011-01795
Jones, D. R., Anderson, K. E., & Musgrove, M. T. (2011). Comparison of environmental and egg microbiology associated with conventional and free-range laying hen management. Poultry Science, 90, 2063–2068. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2010-01139
Jones, D. R., Cox, N. A., Guard, J., Fedorka, P. J., Buhr, R. J., Gast, R. K., Abdo, Z., Rigsby, L. L., Plumblee, J. R., Karcher, D. M., Robinson, C. I., Blatchford, R. A., & Makagon, M. M. (2015). Microbiological impact of three commercial laying hen housing systems. Poultry Science, 94, 544–551. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/peu010
Jones, D. R., Karcher, D. M., & Abdo, Z. (2014). Effect of a commercial housing system on egg quality during extended storage. Poultry Science, 93, 1282–1288. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2013-03631
Karcher, D. M., Jones, D. R., Abdo, Z., Zhao, Y., Shepherd, T. A., & Xin, H. (2015). Impact of commercial housing systems and nutrient and energy intake on laying hen performance and egg quality parameters. Poultry Science, 94, 485–501. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/peu078
Kenji, J. (2010, August 27). The Food Lab: do better eggs really taste better? Serious Eats. http://www.seriouseats.com/2010/08/what-are-the-best-eggs-cage-free-organic-omega-3s-grocery-store-brand-the-food-lab.html
Ketta, M., & Tůmová, E. (2016). Eggshell structure, measurements, and quality-affecting factors in laying hens: A review. Czech Journal of Animal Science, 61(7), 299–309. https://doi.org/10.17221/46/2015-CJAS
Kosmidou, M., Sossidou, E., Fortomaris, P., Yannakopoulos, A., & Tserveni-Goussi, A. (2009, June 23-26). Sensory evaluation of eggs produced by free-range hens foraging in pastures enriched with Ocimum basilicum and Mentha spicata [Conference Presentation]. European Symposium on the Quality of Eggs and Egg Products, Prague, Czech Republic. https://www.cabi.org/Uploads/animal-science/worlds-poultry-science-association/WPSA-turkey-2009/19_kosmidou_mps2009.pdf
Mizumoto, E. M., Canniatti-Brazaca, S. G., & Machado, F. M. (2008). Chemical and sensorial evaluation of eggs obtained by different production systems. Food Science and Technology, 28(1), 60–65. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-20612008000100010.
Moats, W. A. (1980). Classification of bacteria from commercial egg washers and washed and unwashed eggs. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 40(4), 710–714.
Mugnai, C., Del Bosco, A., & Castellini, C. (2009). Effect of rearing system and season on the performance and egg characteristics of Ancona laying hens. Italian Journal of Animal Science, 8(2), 175–188. https://doi.org/10.4081/ijas.2009.175
Musgrove, M. T., Jones, D. R., Shaw, J. D., Sheppard, M., & Harrison, M. A. (2009). Enterobacteriaceae and related organisms isolated from nest run cart shelves in commercial shell egg processing facilities. Poultry Science, 88, 2113–2117. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2009-00021
Parisi, M. A., Northcutt, J. K., Smith, D. P., Steinberg, E. L., & Dawson, P. L. (2015). Microbiological contamination of shell eggs produced in conventional and free-range housing systems. Food Control, 47, 161–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.06.038
Peña, M., Castro, A. C., & Martínez, T. (2011). Conocimientos, opiniones y prácticas respecto al huevo de gallina en familias de comunidades urbana-rural, Costa Rica. Revista Costarricense de Salud Pública, 20(1), 32–39.
Perić, L., Dukic, M., & Bjedov, S. (2016). Effect of production systems on quality and chemical composition of table eggs. The Serbian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 65(3), 27-31. https://doi.org/10.1515/contagri-2016-0014
Poder Ejecutivo. (2006). Decreto Nº 33115 de 2006. Reglamento técnico de Costa Rica 397:2006: Huevos frescos o refrigerados de gallina para consumo humano. Ministerio de Agricultura y Ganadería. http://www.mag.go.cr/legislacion/2006/de-33115.pdf
Poder Ejecutivo. (2018). Decreto N° 41420 de 2018: Reglamento técnico centroamericano RTCA 67.04.50:17: Alimentos. Criterios microbiológicos para la inocuidad de los alimentos. Ministerio de Comercio Exterior. https://www.comex.go.cr/media/3480/279_anex-243-rtca-67-04-50-08-microbio-may-09.pdf
Pouch, F., & Ito, K. (Eds.) (2001). Compendium of methods for the microbiological examination of foods. American Public Health Association.
Protais, J., Queguiner, S., Boscher, E., Piquet, J. C., Nagard, B., & Salvat, G. (2003, September 23-26). Effect of housing system on the bacterial flora in the air and on egg shells [Conference Presentation]. European Symposium of the Quality of Eggs and Egg Products. France. http://www.wpsa.com/index.php/publications/wpsa-proceedings/effect-of-housing-systems-on-the-bacterial-flora-in-the-air-and-on-egg-shells/viewdocument/3494
Ruiz, B. (2020). Fuerte crecimiento de la avicultura latinoamericana en 2019. Industria Avícola, 67(3), 4–25.
Sharaf Eddin, A., Ibrahim, S., & Tahergorabi, R. (2019). Egg quality and safety with an overview of edible coating application for egg preservation. Food Chemistry, 296, 29–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.05.182
Singh, R., Cheng, K. M., & Silversides, F. G. (2009). Production performance and egg quality of four strains of laying hens kept in conventional cages and floor pens. Poultry Science, 88, 256–264. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2008-00237
Smeltzer, T. I., Orange, K., Peel, B., & Runge, G. I. (1979). Bacterial penetration in floor and nest box eggs from meat and layer birds. Australian Veterinary Journal, 55, 592–593. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-0813.1979.tb07055.x
Smith, A., Rose, S. P., Wells, R. G., & Pirgoziieb, V. (2000). The effect of changing the excreta moisture of caged laying hens on the excreta and microbial contamination of their egg shells. Poultry Science, 41, 168–173. https://doi.org/10.1080/713654903
Stojanova, M., Kocevski, D., Vukovic, V., & Porcu, K. (2016). Comparison of qualitative properties of eggs from hens reared in battery cages and free range system. International Journal of Agronomy and Agricultural Research, 9(6), 77–83. https://www.innspub.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/IJAAR-V9No6-p77-83.pdf
Sulimova, L., Zhuchaev, K., & Kochneva, M. (2020). Poultry behavior reactions and welfare. Sel’skokhozyaistvennaya Biologiya, 55(2), 209–224. http://www.agrobiology.ru/2-2020sulimova-eng.html
Svobodová , J., & Tůmová, E. (2014). Factors affecting microbial contamination of market eggs: a review. Scientia Agriculturae Bohemica, 45(4), 226–237. https://doi.org/10.1515/sab-2015-0003
Tercic, D., Zlender, B., & Holcman, A. (2012). External, internal and sensory qualities of table eggs as influenced by two different production systems. Agro-knowledge Journal, 13(4), 555–562. https://doi.org/10.7251/AGREN1204555T
Tomczyk, Ł., Stępień, Ł, Urbaniak, M., Szablewski, T., Cegielska-Radziejewska, R., & Stuper-Szablewska, K. (2018). Characterisation of the mycobiota on the shell surface of table eggs acquired from different egg-laying hen breeding systems. Toxins 10(7), Article 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10070293
Tůmová, E., & Ebeid, T. (2003). Effect of housing system on performance and egg quality characteristics in laying hens. Scientia Agriculturae Bohemica, 34, 73–80.
Tůmová, E., Englmaierová, M., Ledvinka, Z., & Charvatova, V. (2011). Interaction between housing system and genotype in relation to internal and external egg quality parameters. Czech Journal of Animal Science, 56(11), 490–498. https://doi.org/10.17221/3838-CJAS
Yenice, G., Kaynar, O., Ileriturk, M., Hira, F., & Hayirli, A. (2016). Quality of eggs in different production systems. Czech Journal of Food Science, 31(4), 370–376. https://doi.org/10.17221/33/2016-CJFS
Wilson, A., Chandry, S., Turner, M. S., Courtice, J. M., & Fegan, N. (2021). Comparison between cage and free-range egg production on microbial composition, diversity and the presence of Salmonella enterica. Food Microbiology, 10, Article 103754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2021.103754

Archivos adicionales
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
1. Política propuesta para revistas de acceso abierto
Los autores/as que publiquen en esta revista aceptan las siguientes condiciones:
- Los autores/as conservan los derechos morales de autor y ceden a la revista el derecho de la primera publicación, con el trabajo registrado con la licencia de atribución, no comercial y sin obra derivada de Creative Commons, que permite a terceros utilizar lo publicado siempre que mencionen la autoría del trabajo y a la primera publicación en esta revista, no se puede hacer uso de la obra con propósitos comerciales y no se puede utilizar las publicaciones para remezclar, transformar o crear otra obra.
- Los autores/as pueden realizar otros acuerdos contractuales independientes y adicionales para la distribución no exclusiva de la versión del artículo publicado en esta revista (p. ej., incluirlo en un repositorio institucional o publicarlo en un libro) siempre que indiquen claramente que el trabajo se publicó por primera vez en esta revista.
- Se permite y recomienda a los autores/as a publicar su trabajo en Internet (por ejemplo en páginas institucionales o personales) antes y durante el proceso de revisión y publicación, ya que puede conducir a intercambios productivos y a una mayor y más rápida difusión del trabajo publicado (vea The Effect of Open Access).